For this reason, variable costs are a required item for companies trying to determine their break-even point. In addition, variable costs are necessary to determine sale targets for a specific profit target. The company faces the risk of loss if it produces less than 20,000 units. However, anything above this has limitless potential for yielding benefits for the company. Therefore, leverage rewards the company for not choosing variable costs as long as the company can produce enough output.
Cost of Goods Sold: Definition, Formula, Example, and Analysis
You can focus resources on those areas, optimizing overall efficiency and resource utilization. A company had provided the details of expenses incurred during the year on the production of 1,000 units of product. For example salaries of employees involving directly in production, cost of direct material, packaging cost, and cost of shipment or delivery. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Cost units are always selected carefully based on the nature of business operations.
What are unit costs?
Solely focusing on the cost of a unit could compromise product quality or perceived value. Cutting costs without considering quality implications can harm customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Effective supplier collaboration can lead to favorable terms, discounts, and stable pricing, influencing costs positively.
What is a service cost center?
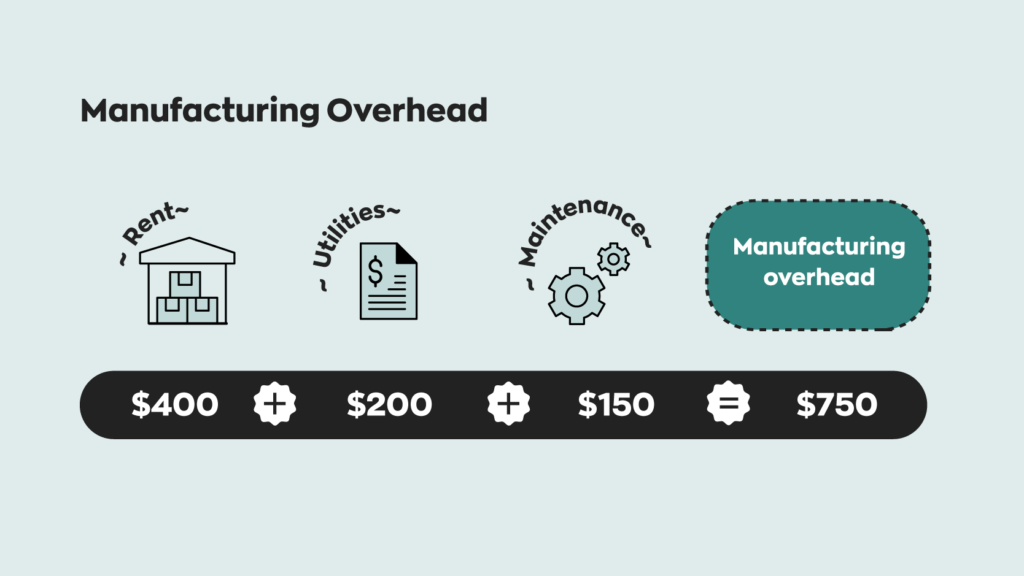
For example, if a logistics company leases a warehouse for storage, the lease cost would be a fixed cost of a unit. Each unit of raw material purchased from the supplier costs the manufacturing company INR what is a cost sheet definition components format 15. Knowledge of this cost-of-unit figure helps assess the viability of the procurement deal. Besides negotiating better terms, you can make informed resource allocation and production planning decisions.
This means that fixed costs are not dependent on the volume of production and remains the same irrespective of the output. The unit cost of production is the total amount of expenses incurred by a company to produce a certain quantity of goods or services and then divide the total amount by the quantity produced. Unit cost is a method of calculating the cost of producing one unit of a product or service. It can be used in various industries, including manufacturing and retail. Unit costs are typically expressed as a dollar amount per unit or can be calculated as a percentage of sales revenue.
Managing fixed and variable costs of production becomes very important as the companies looking to implement different strategies to manage their unit costs. Maintaining a vigilant eye on the cost per unit metric is paramount for businesses due to its far-reaching implications on financial health and competitiveness. When a company accurately calculates and manages its cost per unit, it can set competitive yet profitable prices for its products or services.
- Examples of variable costs are sales commissions, direct labor costs, cost of raw materials used in production, and utility costs.
- Unit cost can be influenced by many factors that shape cost structures and operational efficiencies.
- A production cost center refers to a cost center that is engaged in regular production (e.g. converting raw materials into finished products).
- Perform an in-depth analysis of the operating processes of each responsibility segment.
Unveiling the various components that contribute to the cost of a unit helps identify the key cost drivers within production. The insight enables you to target areas for cost reduction or process improvement. Understanding the impact of changes in input costs or production volume will help implement measures to enhance operational effectiveness. Unit cost is the price a business pays for each unit of a product or service when buying, selling, or storing it.
All public companies are required to use the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) accrual method of reporting, while many private companies elect to do so. Under GAAP they have the responsibility of recording unit costs at the time of production and matching them to revenues through revenue recognition. Goods-centric companies will file unit costs as inventory on the balance sheet at product creation. When the event of a sale occurs, unit costs will then be matched with revenue and reported on the income statement. Unit costs will vary over time and as the scale of a business’ operation changes.
Raw materials are the direct goods purchased that are eventually turned into a final product. If the athletic brand doesn’t make the shoes, it won’t incur the cost of leather, synthetic mesh, canvas, or other raw materials. In general, a company should spend roughly the same amount on raw materials for every unit produced assuming no major differences in manufacturing one unit versus another.
Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. According to the Institute of Cost and Management Accountants, the “operation cost center is a center which consists of those machines and/or persons which carry out the same operations.” When a plant or machine is taken as a unit, it is an impersonal cost center; when a person or group of persons are taken as a unit, the personal cost center is implied. A personal cost center is a cost center that consists of a person or group of persons (e.g., departmental foreman, salesman, supervisor, and factory manager). If costs are accumulated for a person, machine, or department, then this entity will be treated as a cost center.